Ressources / Guide / Push Cameras: Top Options on the Market & More [New for 2025]
Guide
Push Cameras: Top Options on the Market & More [New for 2025]
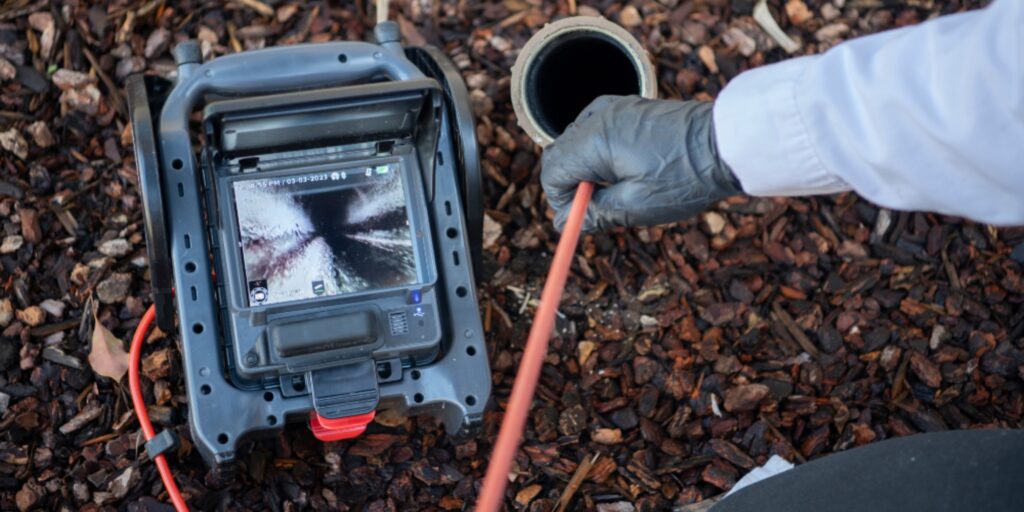
A push camera is a portable, flexible inspection tool equipped with a camera at the end of a long cable, used to visually inspect pipes, ducts, and other hard-to-reach areas.
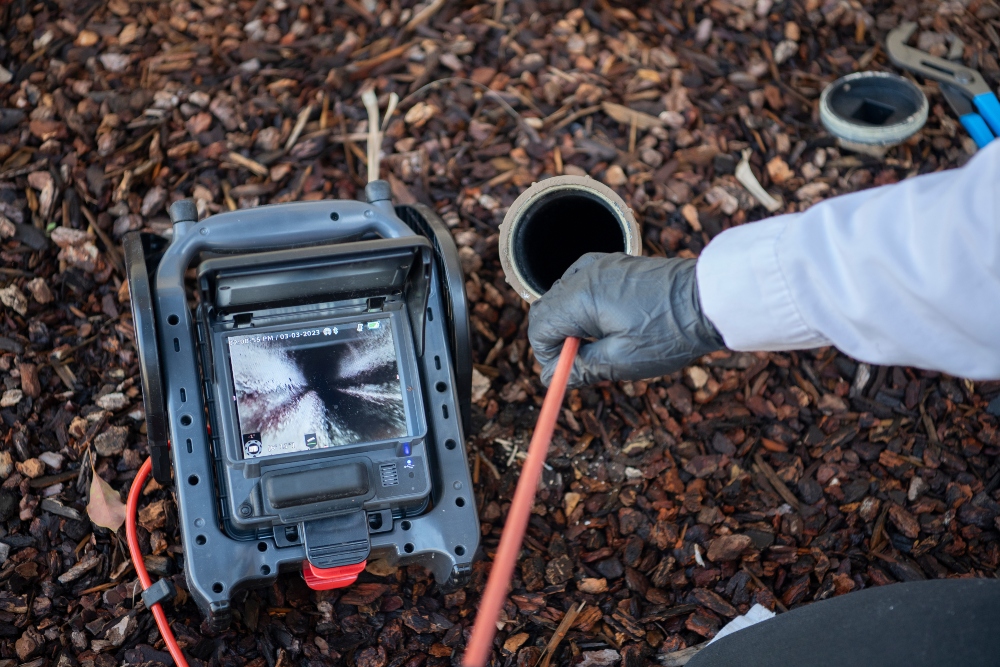

Push cameras provide inspectors with real-time video feedback, enabling technicians to identify blockages, damage, or other issues without costly and disruptive excavation or disassembly.
→ Jump to push cameras for sale and rent.
Common applications for push cameras in heavy industries include:
- Pipeline inspections in Oil & Gas
- Tank inspections in Petrochemical facilities
- Heat exchanger inspections in Power Generation
- Cooling tower inspections in Power Plants
Here are some other common applications for push cameras:
- Sewer and drain line inspections
- HVAC ductwork inspections
- Plumbing system checks
- Chimney inspections
In this guide to push cameras we’ll share the top models on the market, how to do an inspection with a push camera, the industries that use push cameras, and more.
Use the menu to the right to jump around, or keep reading for our list of the top push cameras for sale and rent.
Best Push Cameras for Sale and Rent [New for 2025]
Looking to buy or rent a push camera? Here are our top options for the industrial inspection market.
1. Pearpoint P374 IS
The Pearpoint P374 IS is an intrinsically safe push camera system designed for use in hazardous environments. It provides high-quality imaging in a durable and reliable package, making it useful for industries that require certified equipment.
- What makes it stand out. Intrinsically safe push camera
- Cable length. Up to 150 ft
- Camera head. Self-leveling, wide-angle view
- Caractéristiques principales. ATEX Zone 1 certified, rugged, high-definition imaging
- Applications. Hazardous industrial applications, oil and gas, chemical plants
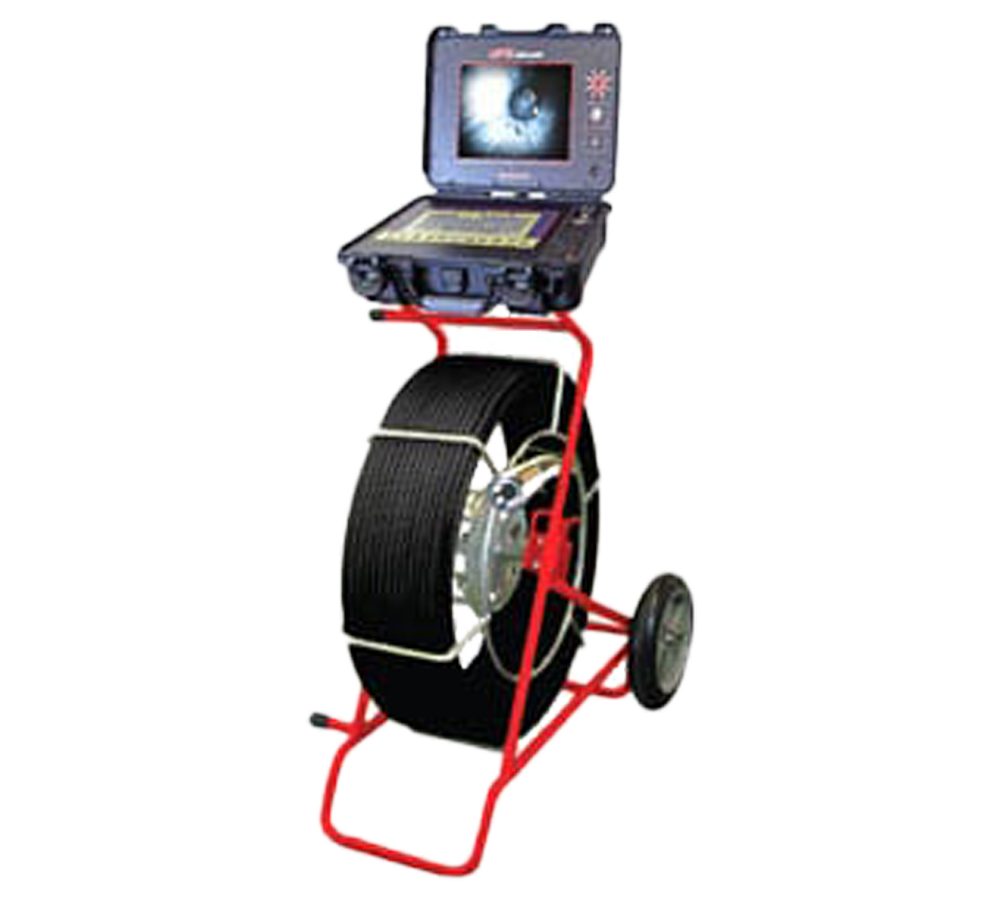
2. Insight Vision Vutek Series
The Insight Vision VuTek Series is a versatile push camera system designed for both general and specialized inspections. It offers high-definition video, various camera head options, and user-friendly operation, making it suitable for numerous industries.
- What makes it stand out. Multi-purpose push camera
- Cable length. Multiple options up to 300 ft.
- Camera head. Interchangeable, various options for different applications
- Caractéristiques principales. High-definition video, durable and easy to use, and available in multiple sizes
- Applications. Pipelines, ductwork, and other industrial inspections
Buy or rent the Insight Vision Vutek.
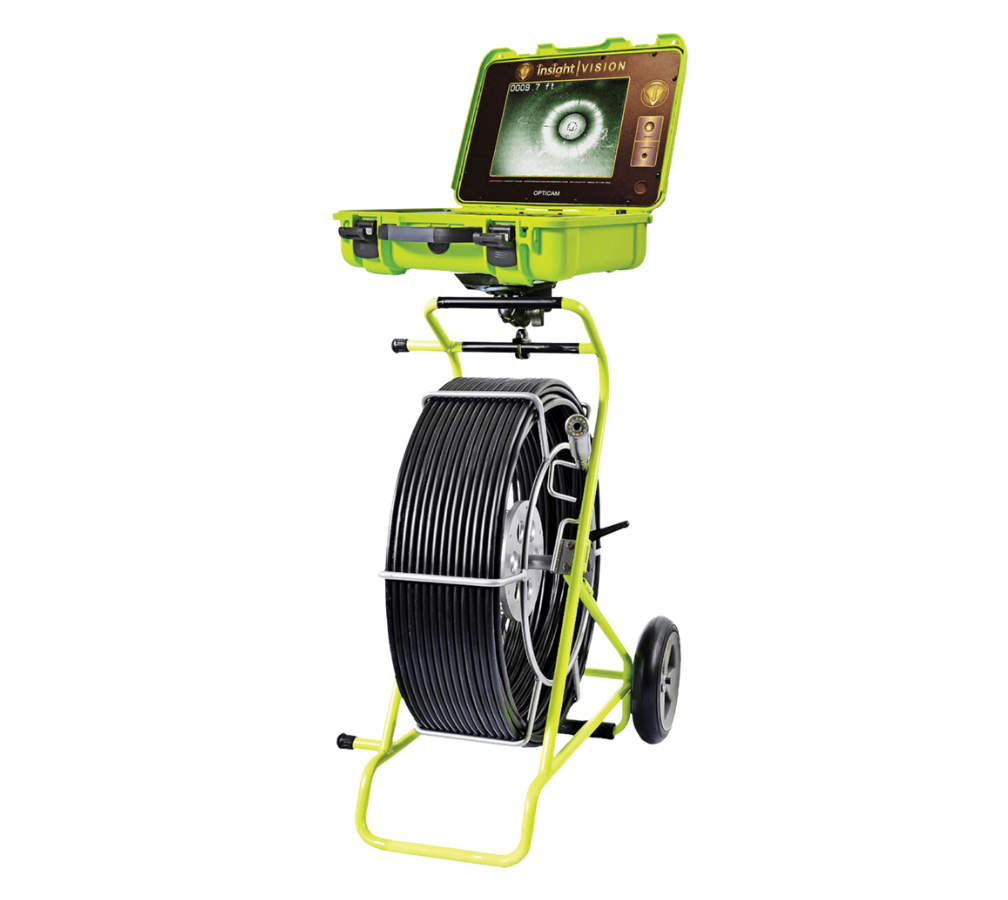
3. Insight Vision Opticam
The Insight Vision Opticam is a versatile push camera system for pipe inspections, offering high-quality visuals and a range of features for efficient data collection.
- What makes it stand out. Push camera with self-leveling color Camera
- Cable length. Up to 400 ft
- Camera head. 1.3″ self-leveling, modular design
- Caractéristiques principales. Real-time Wi-Fi streaming, distance counter, one-touch USB recording
- Applications. Sewer inspections, pipeline assessments, facility maintenance
Buy or rent the Insight Vision Opticam.
4. PipeMaster 200/400
The PipeMaster 200/400 series is a robust and versatile push camera system designed for demanding environments. It offers a range of features for detailed pipe and sewer inspections. The system is available for sale and rent with a variety of cable lengths.
- What makes it stand out. Heavy-duty push camera
- Cable length. Options for 200 ft and 400 ft lengths
- Camera head. Self-leveling, high-resolution
- Caractéristiques principales. Rugged construction, large display, robust cable
- Applications. Pipeline and sewer inspections
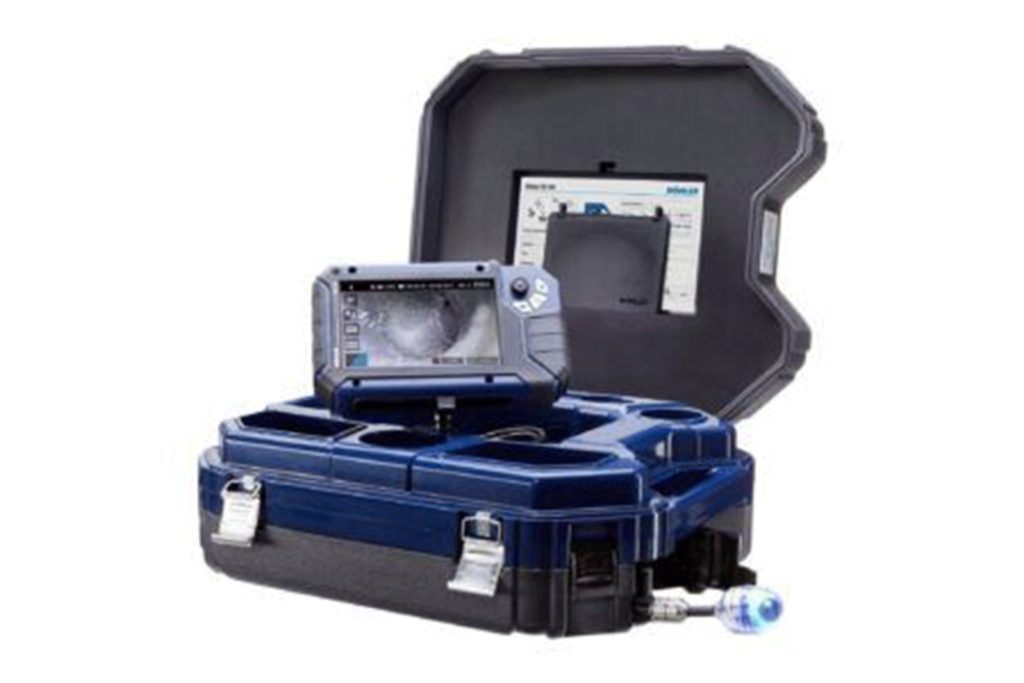
5. Wohler – VIS700
The Wohler VIS700 (HD) is a high-definition push camera system designed for detailed pipe inspections. It features a pan-and-tilt camera head, providing users with enhanced flexibility and precision when navigating challenging pipe configurations. This rugged, durable system is ideal for professional use in various industries.
- What makes it stand out. HD push camera with pan & tilt camera head
- Cable length. Up to 200 ft
- Camera head. HD camera with pan-and-tilt capability for versatile inspections
- Caractéristiques principales. HD imaging, adjustable camera head, long cable reach
- Applications. Pipe and sewer inspections, industrial facilities, HVAC systems
Buy or rent the Wohler VIS700.
6. Wohler – VIS350 PLUS 100′ (30m)
The Wohler VIS350 PLUS is a compact push camera system equipped with a 100′ cable, making it a great choice for tight spaces and short-range inspections. This system offers clear visuals and is engineered for quick and efficient assessments in various environments.
- What makes it stand out. Compact push camera
- Cable length. 100 ft (30m)
- Camera head. High-definition camera with wide-angle view
- Caractéristiques principales. Easy setup, compact design, high-definition imaging
- Applications. Residential plumbing, industrial pipes, vent inspections
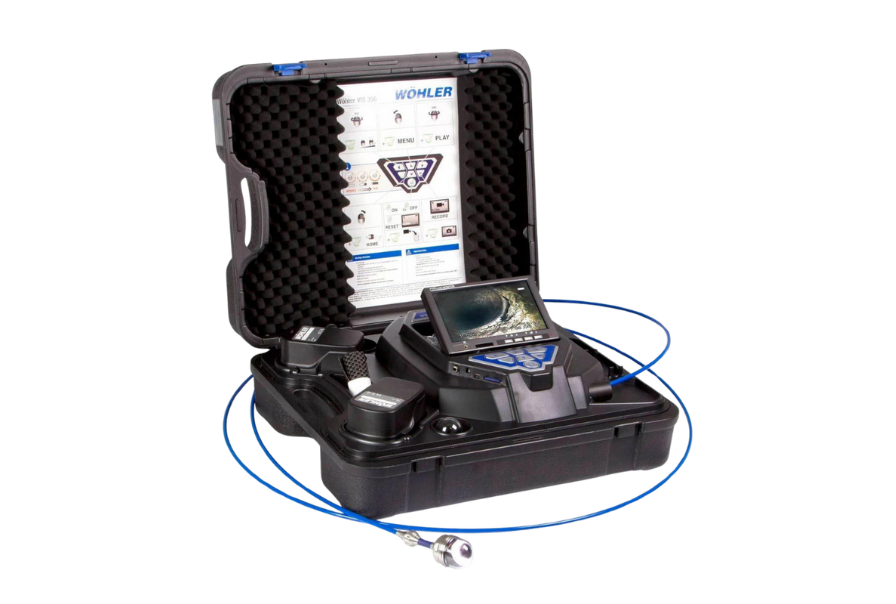
7. Wohler – VIS340 Dual Camera Head 100′ (30m)
The Wohler VIS340 Dual Camera Head is a versatile push camera system featuring a dual-camera head for detailed inspections. The dual-camera setup allows for both front and side viewing, providing comprehensive pipe assessments without the need to reposition the camera.
- What makes it stand out. Push camera with dual camera head
- Cable length. 100 ft (30m)
- Camera head. Dual camera heads for front and side inspections
- Caractéristiques principales. Dual-camera setup, high-definition imaging, flexible use in various pipe sizes
- Applications. Pipe inspections, drain assessments, HVAC system checks
What Is a Push Camera?
A push camera is a portable, flexible inspection tool used to visually examine the interiors of pipes, ducts, or sewer lines, providing real-time video or images for maintenance and diagnostic purposes.
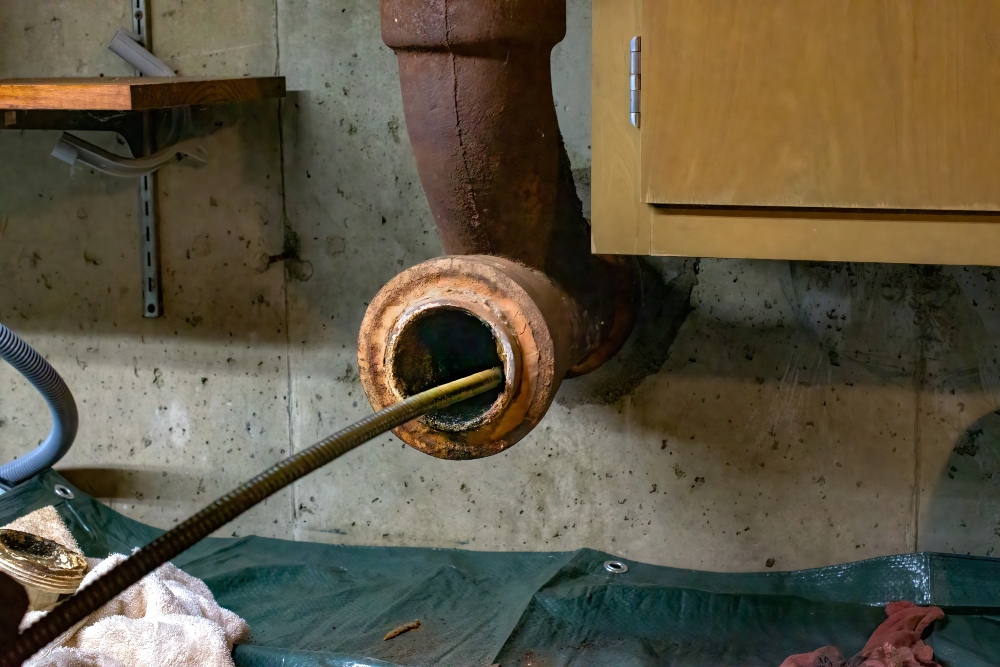

How Push Cameras Work
A push camera consists of a flexible rod with a camera head that is manually pushed into a pipe or sewer line.
The camera head is equipped with LED lights to illuminate the interior and capture real-time video or still images of the pipe’s condition.
The footage is displayed on an attached monitor, allowing technicians to visually inspect the pipe for issues such as blockages, cracks, corrosion, or other structural damage.
This non-invasive method provides critical information for maintenance and repairs without the need for excavation.
Advantages of Using a Push Camera
- Compact and portable. Push cameras are lightweight and easy to transport compared to robotic crawlers, making them ideal for fieldwork.
- Non invasif. Push cameras allow for thorough inspections without the need for digging or disrupting the environment, saving both time and costs.
- Polyvalent. These cameras can be used for pipes of various diameters and lengths, typically ranging from 150 to 490 feet, making them suitable for a wide range of inspection tasks.
- High-quality imaging. Many push cameras feature HD video recording, self-leveling cameras, and pan-and-tilt capabilities, ensuring detailed and clear inspection results.
- Rentabilité. Push cameras are more affordable than other inspection methods, such as robotic crawlers, offering a budget-friendly option for detailed inspections.
Applications of Push Cameras
Push cameras are widely used across industries for a variety of inspection tasks. Some common applications include:
- Sewer and pipeline inspections. Used to detect blockages, leaks, and corrosion in pipes and sewers, helping to prevent expensive repairs and ensure smooth operations.
- HVAC system checks. Inspections of ventilation and ductwork to ensure air quality and system efficiency.
- Industrial and commercial facility assessments. Inspecting hard-to-reach areas in large systems, such as cooling towers or boilers, to ensure they are in good working condition.
Limitations of Push Cameras
While push cameras offer significant advantages, they also come with limitations.
For example, the flexibility of the rod can make it difficult to inspect areas with sharp bends or extreme distances. Also, they’re not always a good option for very large pipes or infrastructure where robotic crawlers are more effective.
All this being said, for many inspection tasks, push cameras remain an ideal, cost-effective solution.
How to Do an Inspection with a Push Camera
Using a push camera effectively requires careful planning, execution, and data analysis.
Here are the key steps.
Step-by-Step Guide to Push Camera Inspections
- Pre-inspection planning.
- Identify the inspection area. Clearly define the area you need to inspect (e.g., specific section of pipeline, type of duct, or area of a vessel).
- Gather relevant information. Collect any available schematics, prior inspection reports, or other relevant data that will help in planning the inspection.
- Select the appropriate push camera. Choose a camera with the right cable length, camera head size, and features to meet your specific needs. Consider factors like cable stiffness, which can affect maneuverability in certain environments.
- Prepare the equipment. Check all camera components, cable connections, and recording devices. Ensure batteries are fully charged, and memory storage is available.
- Site setup.
- Access points. Identify the entry point for the push camera. If necessary, clean the area to reduce obstructions.
- Safety precautions. Implement safety measures, such as proper ventilation, barricading, and wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) as required by the environment. This is especially important when accessing confined spaces.
- Monitor setup. Position the monitor for optimal visibility during the inspection. Secure it safely to avoid any accidents.
- Performing the inspection.
- Insert the camera. Gently push the camera cable into the inspection area. Avoid forcing it as this could damage the equipment or the asset being inspected.
- Navigate slowly and methodically. Maneuver the camera carefully through the inspection area, ensuring all sections of the asset or area are covered. Avoid jerky movements to maintain a clear view.
- Monitor the live video feed. Observe the real-time video on the monitor, and note any areas of concern.
- Record relevant data. Use the camera’s recording feature to capture video and still images of areas needing closer attention. Most modern systems will overlay data like distance traveled, which is useful for analysis.
- Use lighting effectively. Use the built-in lighting to improve visibility in dark or poorly lit areas. Adjust lighting intensity as needed.
- Post-inspection activities.
- Retrieve the camera. Gently pull the camera back, being mindful to avoid snagging the cable.
- Data review. Review the recorded video and images on the monitor or computer to document all notable findings.
- Report generation. Prepare a detailed inspection report that includes all relevant data. Indicate the location and nature of any identified issues, and include video and still images as supporting documentation.
- Equipment maintenance. Clean and store the push camera in a dry place, and replace any damaged or worn parts as needed.
What to Look For During an Inspection
While conducting a push camera inspection, look for the following types of data:
- Corrosion. Note the presence of rust, pitting, and other forms of corrosion on the surface of the equipment or pipeline.
- Cracks and fractures. Identify the location, size, and extent of any cracks or fractures in the material.
- Blockages. Check for any obstructions or blockages that may impede the flow in pipelines, ducts, or other systems.
- Debris build-up. Observe any accumulation of dirt, rust, or other foreign objects within the inspection area.
- Intégrité de la soudure. Look for any defects, discontinuities, or issues with welded connections and/or joints.
- Material degradation. Assess the overall condition of the material, noting any signs of wear, erosion, or other forms of degradation.
- Joint misalignment. Check for any misalignment at pipe joints, fittings, or connections.

Real-World Considerations for Push Camera Inspections
Based on real-world use cases, keep the following in mind:
- Difficult entry points. Often, industrial inspections involve access points that are not in ideal conditions. Be prepared to clear the way or adjust your approach to get a proper assessment.
- Varying material conditions. Inspection areas might be made of a variety of materials, each of which can have a unique impact on inspection results. For example, smooth metal pipes provide a cleaner view than corroded concrete.
- Lighting and visibility. The lighting in industrial settings can vary. Always start with the camera’s built-in lighting. If more light is needed, plan for an additional light source.
- Interprétation des données. When multiple technicians are analyzing the footage, there may be differences in interpretation. For consistency and proper reporting, it’s essential to clearly define data interpretation guidelines.
- Cable management. For long runs, proper cable management is crucial to prevent tangling and snags. Using a reel or other cable management system can make inspections safer and more efficient.
- Durée de vie de la batterie. Always be mindful of battery life, as inspections can take an extended period. Having extra charged batteries on hand can prevent losing critical data.
- Documentation appropriée. Proper documentation is essential to ensure compliance, maintain records, and make repair decisions. Be sure to fully record and interpret all data.
Key Features of Push Cameras
When selecting a push camera, several key features should be considered to ensure it meets the demands of the job.
Below are the most important features to keep in mind when choosing the right push camera for your needs.
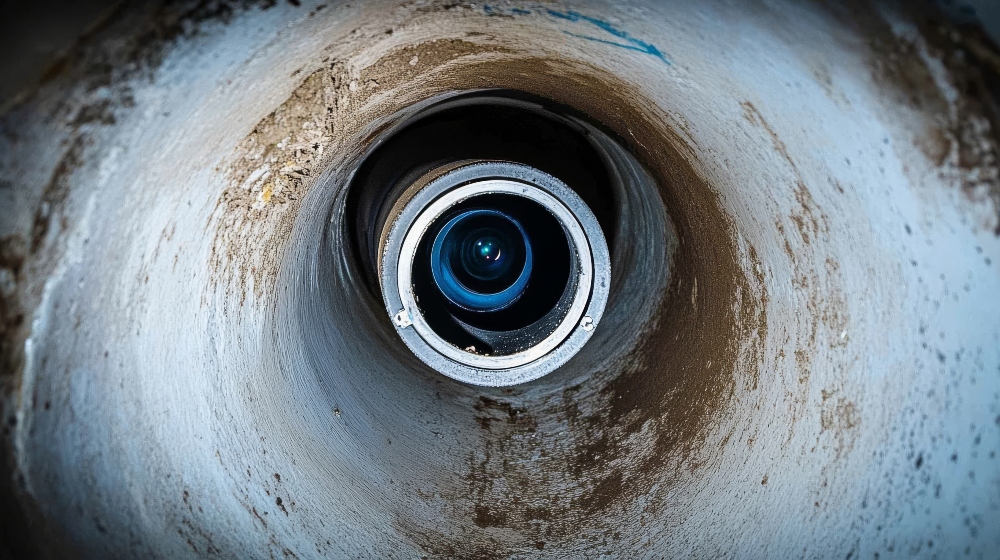

1. Cable Length
The length of the push cable determines how far the camera can travel into a pipe or duct. Common lengths range from 50 feet to 300 feet or more, depending on the application. Consider the typical distances you’ll need to cover and choose a cable length that offers ample reach.
For cable length, keep in mind:
- Models with longer cable lengths are ideal for larger properties or commercial facilities, where a lot of distance needs to be covered.
- Shorter cable lengths are better suited for residential inspections or smaller, more contained spaces.
2. Camera Head Size
The diameter of the camera head plays a crucial role in navigating tight spaces. Smaller camera heads are ideal for narrow pipes and ducts, while larger heads may provide better image quality in larger spaces.
For camera head size, keep in mind:
- Smaller camera heads are best for inspecting narrow drains or pipes that may have tight bends.
- Larger camera heads are more appropriate for wide pipes where image quality is a priority.
3. Image Quality and Display
A high-resolution camera and display are essential for clear and accurate inspections. Look for cameras with a good sensor and a monitor that provides crisp visuals, even in low-light conditions.
For image quality and display, keep in mind:
- High-resolution cameras help to detect small defects or blockages that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Models with larger and brighter displays ensure that you can clearly see inspection footage, even in poorly lit environments.
4. Recording Capabilities
Many push cameras offer the ability to record video and capture still images. This feature is invaluable for documentation and further analysis. Look for models with ample storage and easy transfer options.
For recording capabilities, keep in mind:
- Recording capabilities are vital for documentation, making it easier to track inspections and share findings with clients or teams.
- Look for cameras with options to easily transfer video files via USB, SD card, or cloud storage for convenience.
5. Durability and Construction
Push cameras are often used in harsh environments. Look for models with robust construction, waterproof camera heads, and durable cables that can withstand the rigors of field use.
For durability and construction, keep in mind:
- Durable models are ideal for use in tough, outdoor environments or industrial settings where equipment may face rough conditions.
- Waterproof cameras are essential for inspecting pipes or ducts in wet or flooded environments.
6. Lighting
Integrated lighting, such as LED lights, illuminates the area being inspected, which is essential for clear visibility in dark environments.
For lighting, keep in mind:
- Push cameras with adjustable lighting provide the flexibility to inspect dark or poorly lit areas.
- LED lights are typically energy-efficient, providing long-lasting illumination for extended inspection sessions.
Push Cameras in Oil & Gas
In Oil and Gas, push cameras are vital for maintaining the integrity of pipelines, storage tanks, and other critical infrastructure.

They enable thorough visual inspections to identify potential issues such as corrosion, cracks, and blockages, preventing costly downtime and ensuring operational safety. These inspections are crucial for regulatory compliance and maintaining asset integrity.
Here are some of the key ways push cameras are used in Oil and Gas:
1. Pipeline Weld Inspections
Push cameras are used to inspect welds in pipelines, an essential task in the oil and gas industry where the safety and integrity of pipelines are paramount.
These inspections help identify potential weaknesses in the welds that could lead to cracks, leaks, or failures. Early detection of such issues ensures that corrective actions can be taken before they lead to catastrophic failures.
2. Internal Tank Inspections
Storage tanks in the oil and gas industry often contain volatile substances, making regular internal inspections critical for safety.
Push cameras are ideal for inspecting the interior of tanks for signs of corrosion, wear, or contamination. These inspections can be performed without having to manually enter the tanks, enhancing safety and reducing the time required for maintenance.
3. Heat Exchanger Tube Inspections
Heat exchangers are crucial for maintaining temperature control in various oil and gas operations.
Push cameras are used to inspect the internal tubes of heat exchangers for blockages, corrosion, or damage. Regular inspections help ensure these systems operate efficiently and prevent costly shutdowns due to unexpected failures.
4. Offshore Platform Structural Inspections
Offshore platforms are exposed to harsh marine environments, which can lead to wear and damage over time. Push cameras provide a way to inspect the structural integrity of offshore platforms, including the legs, supports, and pipelines.
These inspections help identify signs of corrosion, cracks, or other issues that could compromise the platform’s safety and operational capabilities.
Push Cameras in Power Generation
The power generation sector uses push cameras extensively for inspecting boilers, turbines, condensers, and other critical equipment.

They allow for the visual assessment of components without the need for complete disassembly, which can save time and reduce costs. Regular inspections are necessary to ensure smooth operations and prevent unexpected failures.
Here are some of the main ways push cameras are used in Power Generation:
1. Boiler Inspections
Boilers in power plants are crucial for generating steam and heat. Push cameras are used to inspect the interior of boiler tubes and components, detecting signs of corrosion, blockages, or scale buildup.
Regular inspections help to ensure the boiler operates efficiently and safely, preventing unexpected failures that could result in costly downtime.
2. Cooling Tower Inspections
Cooling towers are vital for dissipating heat from the power generation process.
Push cameras are ideal for inspecting cooling tower internals, including drift eliminators, fill packs, and distribution systems. These inspections help identify issues like scale buildup, blockages, or corrosion that can impair the cooling process and reduce efficiency.
3. Transformer Inspections
Transformers in power plants must be regularly inspected to ensure they operate at optimal levels. Push cameras are used to inspect transformer components such as bushings, insulation, and bushings for any signs of damage, wear, or overheating.
These inspections help prevent electrical failures, enhancing the reliability and safety of the plant’s electrical systems.
4. Turbine Inspections
Turbines are critical components in power generation, and their performance is essential to the plant’s overall efficiency. Push cameras are used to inspect turbine blades, bearings, and other internal components to detect any signs of damage or wear.
Early detection of problems in turbines allows for preventive maintenance, avoiding costly downtime and extending the life of the equipment.
Push Cameras in the Chemical & Petrochemical Industry
Push cameras are key tools in the chemical and petrochemical industries, where safety, efficiency, and precision are critical.

These industries often deal with hazardous materials, complex pipelines, and hard-to-reach areas, making inspections both challenging and essential.
Here are some of the main ways push cameras are used in the Chemical & Petrochemical Industry:
1. Pipeline and Tank Inspections
In chemical and petrochemical plants, pipelines and tanks are essential for transporting hazardous substances. Push cameras are used to inspect the integrity of these pipelines, helping to detect blockages, leaks, or signs of corrosion.
Regular inspections with push cameras prevent costly spills or damage that could lead to safety risks or production delays.
2. Tank Cleaning and Maintenance
Routine inspections of storage tanks, reactors, and vessels are critical in the chemical industry to ensure cleanliness and prevent contamination.
Push cameras can be inserted into tanks to assess the internal condition of surfaces, identifying corrosion, buildup, or wear without the need to physically enter the tank, which enhances safety and reduces maintenance time.
3. Inspection of Tight and Hard-to-Reach Spaces
Many areas in chemical and petrochemical plants are difficult to access, including tight ducts, pipes, and vent systems. Push cameras excel in these environments by providing visual inspection capabilities in confined spaces.
This is especially valuable for maintaining safety standards and ensuring operational integrity without disassembling complex equipment or risking the safety of workers.
4. Real-time Monitoring
Push cameras equipped with real-time video feed capabilities allow engineers and inspectors to monitor pipeline conditions as the inspection occurs.
This live video enables immediate assessment of any issues, such as leaks or blockages, and ensures swift action can be taken to address potential safety hazards in critical areas of the plant.
5. Preventive Maintenance
By regularly using push cameras for preventive inspections, chemical and petrochemical facilities can identify potential problems early, such as cracks, leaks, or buildups.
This proactive approach helps to prevent unexpected failures, reduce unplanned downtime, and ensure that operations continue smoothly and safely, avoiding the costly consequences of equipment breakdowns or safety incidents.
Other Industrial Applications for Push Cameras
As you can see from the sections above, push cameras are critical tools for visual inspections across heavy industries.
Their ability to access confined spaces and provide real-time feedback makes them essential for maintenance, quality control, and safety.
But those aren’t the only sectors where they’re used—here are some of the other industries that rely on them.
1. Push Cameras in Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, push cameras are used to inspect aircraft engines, wings, and fuselages. This is essential for quality control and preventative maintenance, helping to identify defects and potential points of failure.
Push camera use cases in Aerospace:
- Engine turbine inspections
- Airframe structural inspections
- Wing spar inspections
2. Push Cameras in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, push cameras play a crucial role in quality control and maintenance. They are used to inspect machinery, vessels, and other equipment, ensuring that they meet the necessary standards. They also help identify wear and tear, corrosion, and other potential issues that could affect the manufacturing process.
Push camera use cases in Manufacturing:
- Internal machinery inspections
- Process piping inspections
- Weld quality assessments
- Inspections des appareils à pression
3. Push Cameras in Mining
The mining industry uses push cameras to inspect various components of mines and related machinery.
They are also used to assess the condition of underground tunnels and related infrastructure. These inspections enable predictive maintenance and help to ensure the safety of mining operations.
Push camera use cases in Mining:
- Mine shaft inspections
- Conveyor belt inspections
- Underground tunnel assessments
- Excavation equipment inspections
Other Applications
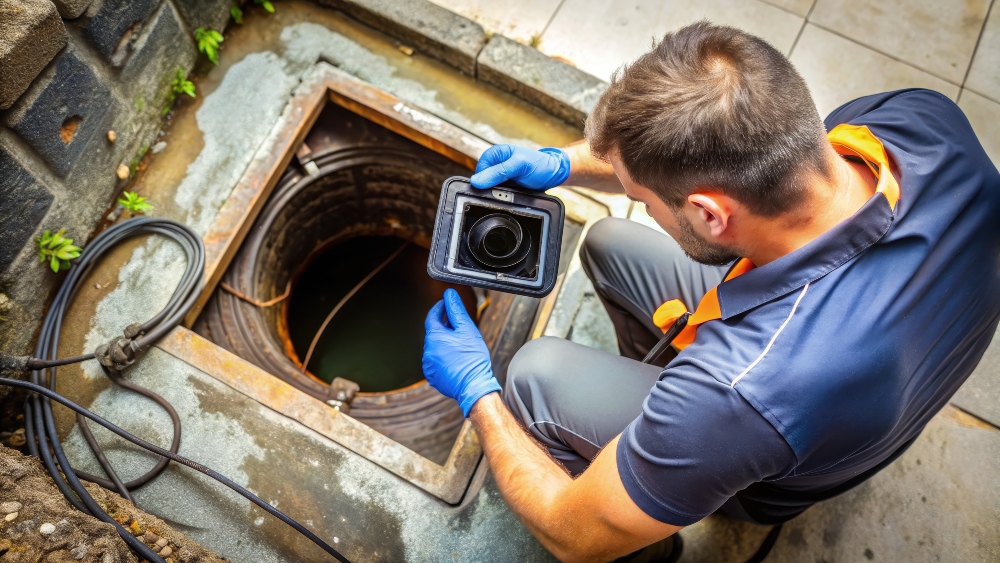
While push cameras are primarily used in industrial contexts, they are also utilized in other settings:
- Sewer and drain line inspections
- HVAC ductwork inspections
- Plumbing system checks
- Chimney inspections

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a push camera?
A push camera is a specialized video camera mounted on a flexible rod or “push cable.” This allows it to be inserted into pipes, ducts, and other confined spaces for visual inspection. The camera provides real-time video feedback, enabling technicians to identify issues without requiring costly disassembly or excavation.
What is the difference between a zoom camera and a push camera?
While both zoom cameras and push cameras are used for visual inspections, they serve different purposes. A zoom camera is usually stationary and can zoom in on objects from a distance. A push camera is designed to be pushed into confined spaces to inspect areas that are otherwise inaccessible. They both provide visual feedback, but zoom cameras inspect from a fixed location while push cameras explore from within.
What are some typical uses for push cameras in industrial settings?
Push cameras are commonly used for inspecting pipelines, storage tanks, heat exchangers, machinery, and other industrial equipment. They are valuable tools in the oil and gas, power generation, manufacturing, mining, and aerospace sectors. The primary focus is on identifying potential issues and ensuring the integrity of industrial assets.
How do I choose the right push camera for my needs?
Choosing the right push camera depends on the specific application. Key considerations include the diameter and length of the inspection area, the type of environment, the need for specific features (like self-leveling camera heads or recording capabilities), and any regulatory requirements. You’ll also need to think about budget and the potential need for equipment rentals versus ownership.
What kind of maintenance do push cameras require?
Push cameras require regular cleaning, careful storage, battery maintenance, and routine checks of cables, camera heads, and connections. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for proper maintenance and to schedule periodic servicing with qualified technicians to ensure reliability and longevity.
Can push cameras be used in hazardous environments?
Yes, some push cameras are designed to be intrinsically safe and can be used in hazardous environments, such as those containing flammable gases or vapors. These systems are typically certified to meet specific safety standards, such as ATEX or IECEx, and should be chosen when safety regulations are of concern.
Is it better to rent or buy a push camera?
The decision to rent or buy a push camera depends on how often you need it. If you’re an industrial company with regular inspection needs, buying may be more cost-effective in the long term. However, if you have occasional or short-term needs, renting can be a more economical solution. Renting also gives you access to a variety of different models without a significant capital investment. Also, rentals can often offer options for maintenance and repairs, reducing any costs on that front.







