
Ressources / Guide / Qu'est-ce que Quad OA ? Votre guide de conformité à l'EPA OOOOa
Guide
Qu'est-ce que Quad OA ? Votre guide de conformité à l'EPA OOOOa
OOOOa, also known as Quad OA, is a set of regulations introduced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to address methane emissions and other air pollutants from the Oil and Gas industry.
The full name of the federal regulations in which the standards are found is 40 CFR Part 60, Subpart OOOOa.
→ Jump to Quad OA-compliant OGI cameras.
As part of the New Source Performance Standards (NSPS), EPA OOOOa targets emissions from new, modified, and reconstructed equipment and processes in the sector.

The primary objective of OOOOa is to monitor and control methane leaks, a potent greenhouse gas, to reduce environmental impact and improve air quality.
The regulation mandates regular leak detection and repair (LDAR), comprehensive reporting, and compliance with strict emission standards for various components, including storage vessels, compressors, and pneumatic controllers.
For the oil and gas industry, adhering to OOOOa ensures not only regulatory compliance but also operational efficiency and enhanced safety by identifying and addressing potential leaks promptly.
In this guide to Quad OA we’ll cover its requirements, OOOOa reporting processes, and compliance strategies to help companies navigate these critical standards effectively.
Use the menu to the right to jump straight to a topic of interest or keep reading for the full guide.
OOOOa-Compliant OGI Cameras
Here at MFE we have developed two OGI cameras that meet the EPA’s 40 CFR part 60 Appendix K requirements as part of OOOOa, b and c.
Both cameras can be carried by a drone.
1. MFE Detect LW Optical Gas Imaging Payload
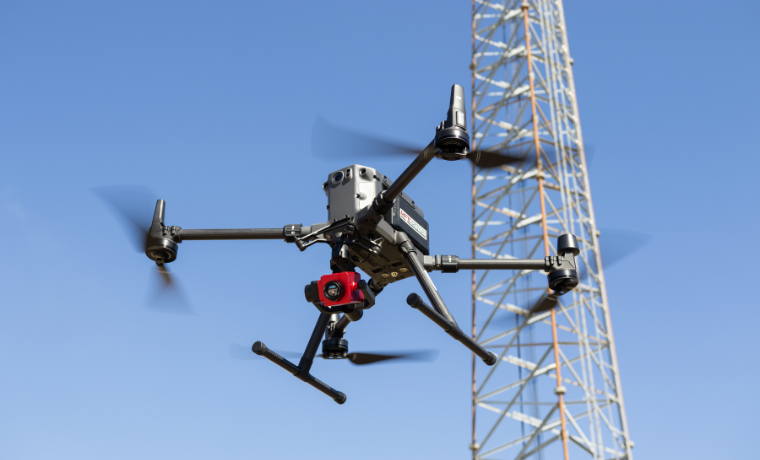

The MFE Detect LW is a pioneering long-wave infrared (LWIR) optical gas imaging camera for DJI M300/M350 drones, designed for effective aerial methane leak detection. Its compliance with OOOOa, b, c, and Appendix K standards makes it essential for industries needing safe, large-scale emissions monitoring.
Caractéristiques principales de l'EMF Detect LW
- High-responsivity uncooled detector for real-time methane visualization.
- Seamless integration with DJI drones for efficient aerial inspections.
- Lightweight, durable design optimized for environmental compliance.
Learn more about the MFE Detect LW.
2. OGI – 640 Optical Gas Imaging Payload
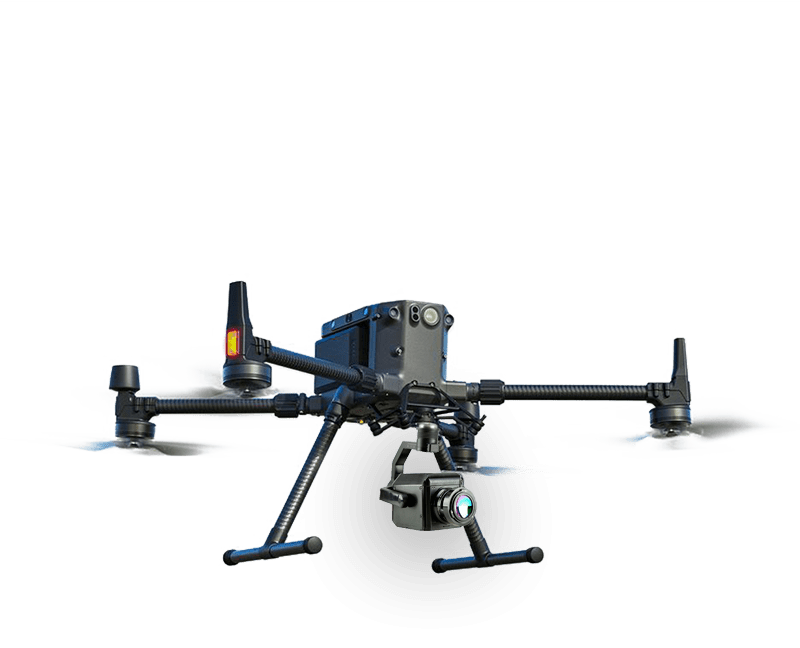
The OGI-640 is designed to integrate seamlessly with a range of drone platforms, providing detailed imaging capabilities for detecting gases like methane and propane. This sensor is critical for industries such as Oil and Gas, where the detection of hydrocarbon leaks can prevent accidents and reduce environmental impact.
Key Features of the OGI-640
- High sensitivity to hydrocarbons.
- Real-time gas imaging.
- Capable of operating in diverse environmental conditions.
Understanding EPA OOOOa Regulations
The EPA OOOOa regulations, officially part of the New Source Performance Standards (NSPS), are designed to reduce methane emissions and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from the Oil and Gas sector.
These rules set stringent requirements for emissions monitoring, leak detection, and repair to ensure environmental compliance and safety.

Key Requirements of EPA OOOOa
- Emissions monitoring. Companies must monitor for methane leaks using approved technologies, such as optical gas imaging (OGI) cameras or other EPA-specified equipment.
- Leak Detection and Repair (LDAR). Regular inspections are required to identify and repair leaks in equipment such as compressors, valves, and storage tanks. The frequency of inspections varies based on equipment type and location.
- Reporting and record keeping. Operators must document inspections, repairs, and emissions data. Accurate and timely submission of reports is essential for maintaining compliance.
- Control equipment standards. Specific equipment, like pneumatic controllers and compressors, must meet performance standards to minimize emissions.
Key Terminology in EPA OOOOa
- Fugitive emissions. Unintended releases of gases from equipment, pipelines, or storage facilities. These emissions are a major target of OOOOa due to their significant environmental impact.
- Applicable sources. Equipment or processes subject to OOOOa regulations, including well sites, compressor stations, and processing plants.
- LDAR programs. Leak Detection and Repair programs are systematic processes for identifying and repairing leaks to comply with EPA standards.
Why OOOOa Compliance Matters
Compliance with OOOOa regulations is critical for Oil and Gas companies since it directly impacts their operations, environmental footprint, and financial stability.
The EPA OOOOa standards set strict requirements for monitoring and controlling methane emissions, ensuring a balance between industrial activity and environmental protection.
Here are four reasons why achieving compliance is important:
1. Avoiding Penalties and Legal Risks
Non-compliance with OOOOa regulations can result in significant financial penalties and legal consequences. Regulatory agencies conduct audits and inspections, and failure to meet standards may lead to costly fines, operational shutdowns, or damage to a company’s reputation. Adhering to the OOOOa compliance guide ensures that businesses avoid these risks and maintain good standing with the EPA.
2. Improving Environmental Impact
The Oil and Gas industry is a major contributor to methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas. By implementing OOOOa monitoring and leak detection programs, companies can significantly reduce emissions, supporting global efforts to combat climate change. This not only aligns with environmental sustainability goals but also enhances public perception and trust in the industry.
3. Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Regular monitoring and maintenance of equipment, as mandated by OOOOa, help companies identify and address issues early. This proactive approach minimizes downtime, reduces energy waste, and extends the lifespan of critical equipment. Ultimately, it improves overall operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
4. Meeting Market and Stakeholder Expectations
In today’s market, stakeholders, investors, and customers increasingly demand environmentally responsible practices. OOOOa compliance demonstrates a company’s commitment to sustainability and regulatory adherence, which can enhance its market position and attract investment.

7 Steps to Achieve OOOOa Compliance
Meeting OOOOa compliance requires a structured, step-by-step approach to ensure you’re addressing all aspects of the rule.
Here are the steps:
1. Identify Applicable Equipment and Sources
Determine which equipment and facilities are subject to EPA OOOOa regulations. This includes well sites, compressor stations, and pneumatic controllers. Categorizing these sources ensures targeted compliance efforts.
Pro tip: Use an asset management system to help you organize and track your assets.
2. Develop an LDAR Program
Establish a comprehensive Leak Detection and Repair (LDAR) program. This involves setting inspection schedules, choosing appropriate detection technologies like optical gas imaging (OGI), and training staff to conduct accurate assessments.
3. Monitor Emissions Regularly
Implement regular emissions monitoring schedules as specified in the OOOOa compliance guide. Use advanced technologies such as OGI cameras or LiDAR systems to detect and quantify methane leaks efficiently.
4. Repair Detected Leaks
Ensure all identified leaks are repaired within the timeframes outlined by EPA OOOOa. Document the repairs, including the date of detection, repair completion, and any follow-up inspections.
5. Maintain Comprehensive Records
Record all monitoring activities, emissions data, and repair actions.
Pro tip: Use an OOOOa reporting template to organize this information and ensure compliance with reporting requirements. See this page on the EPA’s website for reporting templates (search ‘OOOa reporting’).
6. Submit Required Reports
Submit accurate and timely reports to the EPA as part of the regulatory process. This includes data on monitored equipment, detected leaks, and repair actions. Proper reporting ensures transparency and regulatory adherence.
7. Train Employees and Contractors
Provide comprehensive training for employees and contractors involved in OOOOa compliance. This includes understanding the regulations, using detection technologies, and maintaining accurate records.

OOOOa Reporting Requirements
One of the key components of EPA OOOOa compliance is accurate and timely reporting. Proper documentation and submission of data help ensure transparency and demonstrate adherence to regulatory standards.
This section outlines the critical aspects of OOOOa reporting and provides guidance for meeting these requirements.
1. Reporting Deadlines
Reports must be submitted at specified intervals, typically on a semi-annual or annual basis, depending on the facility’s operations. Missing deadlines can result in penalties, so companies should establish a reporting calendar to stay on track.
2. Required Data
- Details of monitored equipment and regulated sources
- Emissions data and leak detection results
- Repair actions, including dates and descriptions
- Technology used for emissions monitoring (e.g., optical gas imaging or LiDAR)
- Verification of compliance with LDAR schedules
3. Using an OOOOa Reporting Template
An OOOOa reporting template can streamline the process by organizing required information into a standardized format.
Many companies use software tools to generate these reports, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
4. Submission Process
Reports are typically submitted to the EPA electronically via their designated systems, such as the Compliance and Emissions Data Reporting Interface (CEDRI).
Ensure all files are properly formatted and complete to avoid delays or rejections.
5. Common Reporting Challenges
Some challenges companies face include inconsistent record-keeping, incomplete data, and misinterpretation of reporting requirements. Address these issues by training personnel, automating data collection, and seeking expert guidance when necessary.

How OOOOa Compliance Impacts the Oil and Gas Industry
Compliance with EPA OOOOa regulations has a significant impact on the Oil and Gas industry, influencing operations, costs, and environmental outcomes.
By addressing methane emissions and implementing stringent monitoring and repair practices, OOOOa compliance drives both challenges and opportunities for companies in the sector.

Cost Implications
Adopting OOOOa compliance measures requires initial investment in advanced monitoring technologies, training personnel, and maintaining compliance records. These costs may include:
- Purchasing or leasing leak detection equipment such as optical gas imaging (OGI) cameras or LiDAR systems.
- Implementing software tools for data management and reporting.
- Hiring or training staff to manage emissions monitoring and repairs.
Operational Adjustments
Meeting OOOOa requirements necessitates changes in daily operations and facility management.
These adjustments include:
- Regular leak detection and repair (LDAR) programs to address fugitive emissions
- Enhanced maintenance schedules to prevent equipment malfunctions
- Integrating emissions monitoring into standard operating procedures
Such operational improvements enhance overall efficiency, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of critical equipment.
Environmental Benefits
One of the most significant impacts of OOOOa oil compliance is the reduction of methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas.
By addressing leaks and improving emissions control, companies contribute to:
- Decreased greenhouse gas emissions and climate change mitigation
- Improved air quality for local communities
- Enhanced industry reputation as environmentally responsible operators
These environmental benefits align with increasing public and regulatory demands for sustainable practices in the energy sector.
Market and Competitive Advantages
Companies that achieve EPA OOOOa compliance may gain a competitive edge by demonstrating their commitment to sustainability and regulatory adherence.
This can lead to:
- Improved relationships with stakeholders, investors, and regulators
- Eligibility for incentives or certifications for environmental performance
- Stronger positioning in markets prioritizing sustainable energy practices
Types of Technology for OOOOa Compliance
Meeting EPA OOOOa requirements requires the use of advanced technologies to ensure efficient and accurate emissions detection.
These tools play a vital role in helping the Oil and Gas industry monitor methane leaks, comply with regulations, and minimize environmental impact.

Below are some of the key technologies used for OOOOa compliance.
1. Optical Gas Imaging (OGI) Cameras
Optical gas imaging cameras are widely used for detecting methane and volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. These cameras use infrared technology to visualize gas leaks that are invisible to the naked eye. These days, gas detection drones can carry OGI cameras, allowing you to collect OGI data remotely.
- Avantages. Real-time detection, portability, and ability to inspect hard-to-reach areas
- Applications. Monitoring equipment like compressors, valves, and storage tanks
- Role in OOOOa Compliance. OGI cameras are an EPA-approved method for leak detection, making them a cornerstone of effective Leak Detection and Repair (LDAR) programs.
2. Portable Gas Detectors
Portable gas detectors are compact devices that measure gas concentrations at specific points. They are often used for localized inspections and verification of emissions levels.
- Avantages. Lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to use
- Applications. Spot-checking equipment and verifying repairs during LDAR activities
- Role in OOOOa Compliance. These detectors provide quick, accurate measurements to ensure compliance with EPA OOOOa standards.
Learn more about gas leak detectors.
3. LiDAR Systems
OOOOa LiDAR systems use Light Detection and Ranging technology to detect and measure methane emissions across large areas. These systems are highly effective for identifying leaks from pipelines, storage facilities, and remote sites.
- Avantages. High-precision detection, ability to monitor large facilities, and suitability for remote operations
- Applications. Comprehensive facility scans, pipeline monitoring, and emissions quantification
- Role in OOOOa Compliance. LiDAR is increasingly recognized as a cutting-edge tool for achieving compliance and enhancing operational efficiency.
4. Continuous Monitoring Sensors
Continuous monitoring sensors are installed at key points in a facility to provide real-time data on methane concentrations. These systems help detect leaks as soon as they occur, reducing the time between detection and repair.
- Avantages. Real-time monitoring, automated alerts, and integration with data analytics platforms
- Applications. Long-term emissions monitoring and high-risk area surveillance
- Role in OOOOa Compliance. Continuous monitoring ensures consistent compliance and reduces the need for frequent manual inspections.
5. Advanced Software for Data Management
Data management software is essential for organizing, analyzing, and reporting emissions data. These tools streamline compliance processes by automating record-keeping and generating OOOOa reporting templates.
- Avantages. Automated workflows, error reduction, and enhanced reporting accuracy
- Applications. Emissions tracking, compliance reporting, and audit preparation
- Role in OOOOa Compliance. Software solutions simplify compliance by ensuring that all required data is captured and submitted on time.
The Future of OOOOa Compliance
As global and national efforts to combat climate change intensify, the EPA OOOOa regulations are expected to evolve, driving significant changes in the Oil and Gas industry’s approach to emissions monitoring and compliance.
These updates will likely include stricter standards, advanced technologies, and expanded state-level requirements, shaping the future of environmental compliance.
Potential Updates to OOOOa Regulations
The EPA continues to assess and update its New Source Performance Standards (NSPS), which include OOOOa.
Future updates may incorporate more rigorous requirements, reflecting technological advancements and the growing emphasis on methane reduction.
These updates could include:
- Enhanced leak detection and repair (LDAR) standards with shorter inspection intervals
- Incorporation of cutting-edge technologies like OOOOa LiDAR and other remote sensing tools
- Revisions to Appendix K requirements, which standardize methods for emissions quantification and reporting
These changes aim to close gaps in the existing framework, improve accuracy in emissions reporting, and promote industry-wide adoption of advanced monitoring technologies.
State-Level Regulations Impacting OOOOa Compliance
In addition to federal requirements, state-level rules are becoming increasingly stringent, adding another layer of complexity for operators.
Operators must stay informed about state-specific regulations to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Key state regulations include:
- California Rule 1178. This rule requires enhanced leak detection for storage tanks and other equipment, with stricter repair timelines than federal OOOOa standards.
- Colorado Regulation 7. Focused on ozone and methane emissions, this regulation mandates frequent inspections and detailed emissions reporting.
- Pennsylvania GP-5A. Covers methane emissions from unconventional natural gas well sites, with stringent requirements for LDAR and emissions reporting.
The Role of Emerging Technologies
Technological innovation is playing a pivotal role in shaping the future of OOOOa compliance. Key advancements include:
- LiDAR systems. LiDAR technology enables high-precision methane detection across wide areas, offering faster and more accurate leak identification.
- Continuous monitoring sensors. These devices provide real-time data on emissions, reducing reliance on periodic inspections.
- AI-powered analytics. Artificial intelligence can analyze emissions data to identify trends, predict potential issues, and optimize LDAR programs.
Adopting these technologies not only ensures compliance but also enhances operational efficiency and reduces costs.
Global Implications and Methane Reduction Goals
The push for stricter methane reduction goals at the global level, including initiatives like the Global Methane Pledge, is influencing the EPA and state regulators to adopt more aggressive standards.
As methane is a potent greenhouse gas, its reduction is critical to achieving climate targets.
This trend is expected to result in:
- More frequent updates to federal and state emissions regulations
- Increased collaboration between governments and industries to develop innovative compliance strategies
- Higher scrutiny of emissions reporting and performance data
OOOOa Compliance FAQ
To help companies understand and navigate EPA OOOOa requirements, here are answers to some frequently asked questions about OOOOa compliance, reporting, and monitoring technologies.
What is OOOOa?
OOOOa, also known as Quad OA, is part of the EPA’s New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) that regulate methane and VOC emissions from new, modified, or reconstructed sources in the oil and gas industry. It mandates emissions monitoring, leak detection, and timely repairs.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with OOOOa?
Failure to comply with EPA OOOOa regulations can result in significant penalties, including monetary fines, operational restrictions, or legal action. Non-compliance may also damage a company’s reputation and delay projects.
How does leak detection work under OOOOa?
Leak detection under OOOOa typically involves the use of approved technologies such as optical gas imaging (OGI) cameras, LiDAR, or ultrasonic detectors to identify fugitive emissions from equipment like valves, pumps, and pipelines.
What is an OOOOa reporting template?
An OOOOa reporting template is a standardized format for organizing and submitting required compliance data to the EPA. It helps companies ensure their reports are complete and meet regulatory standards.
What is the difference between OOOO and OOOOa?
While both OOOO and OOOOa are EPA regulations under NSPS, OOOO focuses on reducing VOC emissions, whereas OOOOa specifically addresses methane emissions in addition to VOCs. OOOOa also includes updated requirements for leak detection and repair (LDAR).
What is the difference between OOOOa and OOOOb?
In essence, OOOOa sets the foundation for methane emissions control, while OOOOob represents an evolution of these standards to address regulatory gaps and adopt improved practices.
The primary difference between OOOOa and OOOOob lies in the scope and focus of the regulations under the EPA’s New Source Performance Standards (NSPS).
While both aim to reduce emissions from the oil and gas sector, they apply to different types of sources and introduce varying requirements:
- OOOOa (Quad OA). This regulation, introduced in 2016, focuses on methane and VOC emissions from new, modified, and reconstructed sources in the oil and gas industry. It mandates leak detection and repair (LDAR), emissions monitoring, and control measures for equipment like compressors, pneumatic controllers, and storage tanks.
- OOOOob (Quad OB). As a proposed or newer standard, OOOOb is designed to update and build upon the requirements of OOOOa. It incorporates more stringent controls, reflects advancements in emissions detection technology, and may expand requirements to cover additional sources or refine existing standards.
Which technologies are approved for OOOOa monitoring?
Approved technologies for OOOOa monitoring include optical gas imaging (OGI) cameras, portable gas detectors, and emerging tools like LiDAR. These technologies help detect and measure methane emissions accurately.
Can OOOOa compliance improve operational efficiency?
Yes, adhering to OOOOa regulations often leads to improved operational efficiency by identifying leaks early, reducing energy waste, and preventing costly equipment failures.
How does OOOOa apply to storage tanks?
Storage tanks under OOOOa regulations must meet specific control standards to minimize emissions. This includes installing vapor recovery systems and conducting regular inspections for leaks and malfunctions.
Are small operators subject to OOOOa requirements?
Yes, small operators with applicable sources, such as wells and compressors, are subject to OOOOa. However, some facilities may qualify for reduced monitoring frequencies based on production levels or other criteria.
How often must inspections be conducted under OOOOa?
The frequency of inspections depends on the equipment and the facility’s classification. For example, well sites typically require quarterly monitoring, but the frequency may vary for low-production facilities.
